Return to Bioenergetic Support Page
Co-Enzyme Q10 in Coronary Insufficiency
In this section I will demonstrate to you that:
· Coronary insufficiency
is associated with CoQ10 deficiency
· CoQ supplementation
is therapeutic in coronary insufficiency, relieving symptoms and improving
functional capacity
· CoQ works by
improving the efficiency of energy metabolism
Coronary insufficiency is associated with CoQ10 deficiency

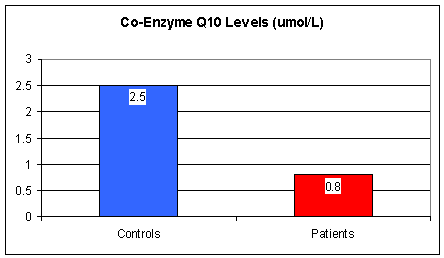
You've seen this graph before. CoQ levels were obtained in normal
volunteers and from patients with symptomatic coronary insufficiency.
Repetitive cardiac tissue oxygen deficiency (as occurs with each episode of
angina) deranges energy metabolism within the heart, wasting CoQ. As the
heart is body's greatest consumer of CoQ, blood CoQ levels will
be low. Studies carried out in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery demonstrate that
heart muscle CoQ levels
are low, and that heart muscle CoQ10 content will rise with supplementation. Basically, the
people who need CoQ the most are the ones with the least amount of it. Then
we doctors step in and put you of drugs (see statin section) that deplete your
CoQ stores even more.
CoQ supplementation is therapeutic in coronary insufficiency
| Baseline | On CoQ | |
| Blood level | 0.95 | 2.2 |
| Treadmill Exercise Time | 345 sec. | 406 sec. |
| Time to ST Depression | 196 sec. | 284 sec. |
| Angina Episodes/Two Weeks | 5.3 | 2.5 |
| NTG Use/Two Weeks | 2.6 | 1.3 |
Coronary patients with stable symptoms were assigned to receive over four weeks either placebo or CoQ 150 mg/day. Placebo therapy had no effect, as you would expect. Angina frequency and NTG need fell sharply with CoQ therapy. Treadmill time increased by 18% and time to ST depression (the EKG sign of supply:demand mismatch for ATP within the heart) increased by 45%
OK - CoQ is therapeutic in coronary insufficiency - but why?
How does CoQ exert its beneficial effect? I was taught that beneficial
therapies in coronary insufficiency either:
· Increased blood flow
to the previously oxygen-starved heart muscle (bypass surgery, angioplasty,
EECP, etc.)
· Decreased the need of
the heart muscle for oxygen (lower HR and BP with drugs, restrict activity
level, etc.)
My shop teacher in eighth grade taught us (boys only, the girls
took home economics) that our cars would last longer and run better if we:
· Took good care of them
· Filled them only with
good fuel
· Made sure that the
fuel contained additives that increased the efficiency of fuel metabolism (oops
- I guess I meant fuel efficiency - eefficiencymetabolism refers to energy processing
within the cells of your body), such that we would get more miles per gallon of
fuel added.
CoQ works by improving the efficiency of energy metabolism
So how does CoQ work? My professors want to know whether it increases blood flow, like an angioplasty, or whether it decreases demand for oxygenated blood, like a drug. My shop teacher might just inquire as to its effect on the efficiency of fuel burning. Who is asking the right question - my professors or my shop teacher?
In this study, patients with stable angina and reproducible
abnormal stress EKG studies were randomized to receive:
· CoQ 600 mg/day over
four days
· Placebo over
four days
· A single 7.5 mg
dose of Pindolol (a beta-blocker) and a 30 mg dose of Isosorbide Dinitrate (a
long-acting nitroglycerin preparation)
Stress studies were carried out at baseline, and after the assigned therapies (in the drug group, the stress test was done 90 minutes following drug administration, when the drug effect was maximal). Subjects were then crossed over to one of the other regimens, such that each subject was tested following each treatment option. The study was blinded, such that the researchers carrying out the stress exams did not know which treatment the study patient had received that day. They looked at cumulative ST depression (the summed up amount of ST depression in the EKG leads monitored during the stress test), or rather change in cumulative ST depression, as a marker of relative treatment efficacy. The findings are presented below, in both individual before and after, and average on treatment values.
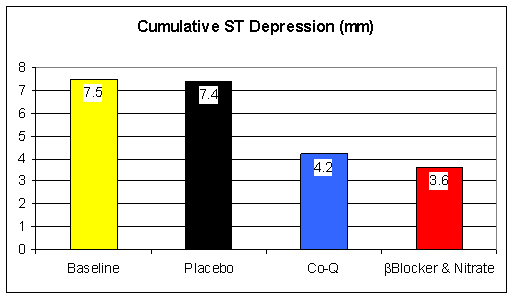
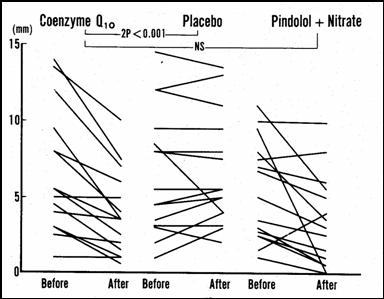
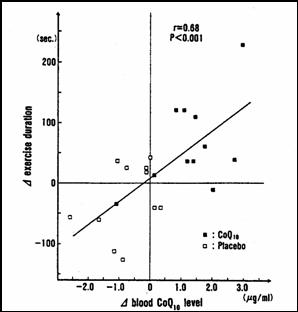
CoQ supplementation over four days worked just as well (no statistically significant difference in treatment efficacy) as did therapy with two prescription drugs. CoQ treatment efficacy is confirmed, but we still don't understand how CoQ works. The researchers hypothesized that CoQ might work like a drug, lowering HR and BP, so they looked at HR and BP at rest and at various points in the stress test:
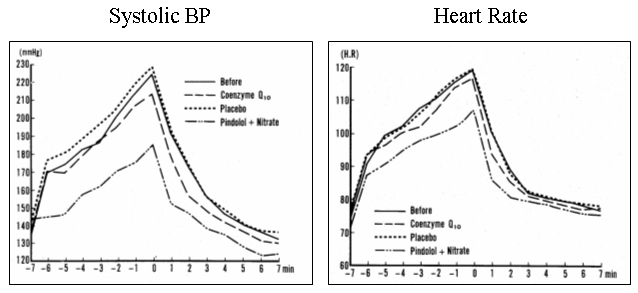
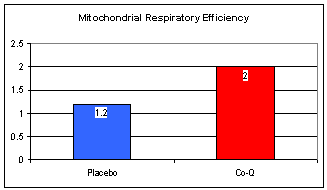
The bottom curve represents two-drug therapy; relative to baseline (no therapy) and placebo therapy , the top two lines, HR and BP were lower at each stage of exercise. The drugs worked, they decreased ST depression, by decreasing the need of the heart for oxygenated blood during effort. Your arteries aren't opening up, but you need less oxygen during effort, so you can do more before you need to stop or take a NTG tablet. CoQ had only a minimal affect on BP and heart rate, but it worked anyways, and just as well as did two-drug therapy. CoQ works because it improves energy metabolism. Just as a fuel additive gives you more "miles per gallon", CoQ gives you more ATP molecules per molecule of oxygen delivered to the heart. These patients were all CoQ deficient (proven to you above), as a consequence of their coronary insufficiency, and now as a contributing cause of their symptoms. Giving them back the CoQ they lacked improved energy metabolism, such that they could make more ATP even in the face of oxygen deficiency, such that they could go longer on the treadmill with less ST depression, reflecting less ischemia with effort. If we did the same study with Carnitine we would see the same result, and if we did the same study with the combination or CoQ and Carnitine we would see a synergy. The graph below on the left shows that the increase in treadmill time (with CoQ the patients could walk farther) is directly related to the change in their CoQ level with supplementation. In other words, the lower your CoQ status pre-treatment, the greater will be your symptomatic and physiologic gain with CoQ treatment. Below right is a graph showing the effect of CoQ supplementation on cellular energy metabolism from heart tissue samples removed at the time of bypass surgery. The bottom line here is that CoQ works by improving the efficiency of energy metabolism. You should take CoQ to improve energy metabolism if your heart is dysfunctional on the basis or coronary disease, cardiomyopathy, or CHF, just as I should take CoQ before running a marathon (which likewise deranges energy metabolism and uses up CoQ). CoQ gives us more ATP per molecule of oxygen.
James C. Roberts MD FACC
1/01/07