Return to the Bioenergetic Support Page
Co-Enzyme Q10 Supplementation in Heart Attack
Randomized, Double Blind Study of Co-Enzyme Q10 Supplementation in Acute Heart Attack
Co-Q10, Selenium, and an Antioxidant Cocktail in Acute Heart Attack
Co-Q10 and Taurine in Acute Heart Attack
Randomized, Double Blind Study of Co-Enzyme Q10 Supplementation in Acute Heart Attack
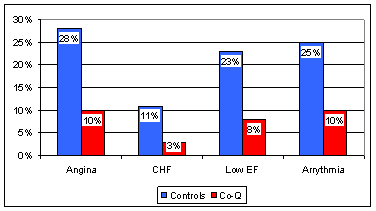
In this study, 144 patients presenting with acute heart attack were randomized to receive Co-Q10 (in a fat soluble gel form) 120 mg/day or placebo. The study was double blind, such that neither the subjects nor the doctors and nurses caring then were aware of the assigned treatment. Event rates at 28 days is given below:

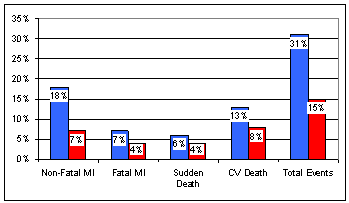
We don't want to see angina soon after a heart attack; this means that you are at risk for further damage. Low EF (ejection fraction) and CHF reflect a larger heart attack, while arrhythmia is associated with an increased risk of sudden death. No wonder the event rate was greater with standard therapy alone. In other words, Co-Q supplementation decreased event rate dramatically, at a cost of about one dollar a day. Event rates at one year post-heart attack are given below:
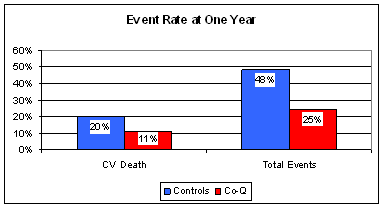
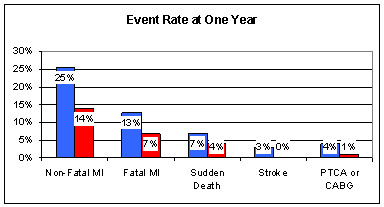
The benefits of Co-Q supplementation were sustained. Death rate fell from 20% to 11%, and total event rate from 48% to 25%. In other words, 9 out of 100 post-heart attack patients who would have died with standard therapy alone were spared simply because they took CoQ10! If a prescription drug decreased any event rate from 4% to 2%, it would be heralded as a medical breakthrough and you would be hearing about it on TV adds during time outs of NFL football games. This miracle drug that provided 50% protection would certainly cost a lot. Co-Q provides fantastic protection for $1/day. But CoQ is not a drug, it is ignored by American physicians, and at the hospitals in Toledo Ohio you are not even allowed to take it. You have to sneak it in.
Co-Q10, Selenium, and an Antioxidant Cocktail in Acute Heart Attack
A related study randomized acute heart attack patients to receive placebo or
a nutritional cocktail consisting of:
· Co-Q10 100 mg and
Selenium 500 mcg within the first 6 hours, followed by
· Co-Q10 100 mg,
Selenium 100 mcg, Zinc 15 mg, Vit C 90 mg, Vit B6 2 mg, and Vit E 15 mg/day over
one year
The point of the study was to see if this antioxidant cocktail had a beneficial effect on the QT interval, the section of the EKG representing electrical repolarization of the heart. The longer the QT interval, the more disordered is repolarization, the greater is the risk for lethal arrhythmia. "Verum" refers to the treated group:
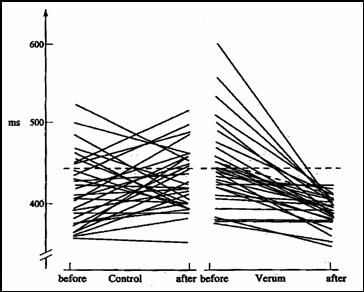
The QT interval increased over time in the standard therapy group, form 415 to 448 msec., while this interval decreased in the antioxidant group, from 440 to 394 msec.
You won't be surprised to see that one year mortality was greater in the placebo group - 21% (6 of 29 subjects), vs. 3% (1 of 32 subjects) in the antioxidant group.
Co-Q10 and Taurine in Acute Heart Attack
Our third study randomized 51 CCU (coronary care unit) patients with suspected heart attack to receive standard therapy alone vs. standard therapy plus Taurine 6,000 mg and Co-Q10 120 mg/day, over 28 days. Acute heart attack and unstable angina are associated with oxidative stress, as both cause and effect. Oxidative stress causes endothelial dysfunction, vasoconstriction, and heightened platelet reactivity, increasing your risk for an acute event. These events themselves generate oxidative stress. Antioxidant levels plummet during a heart attack, as all available antioxidants are "used up" fighting the oxidative fires. With placebo therapy, antioxidant capacity, in this study represented by Vit E and Vit C levels, was low at the onset of heart attack and rose only minimally at 28 days. Conversely, E and C levels rose sharply following CoQ10 and Taurine supplementation.
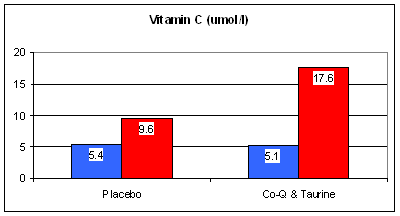
E and C were not administered, but as CoQ10 and Taurine both provide antioxidant protection, other antioxidants, including E and C, were spared, freed up to participate in other repair processes.
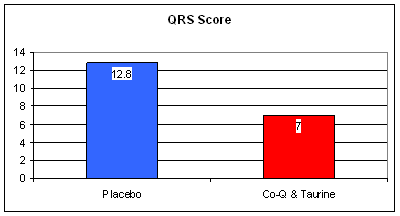
We estimate heart attack size based upon the leak into the circulation of cardiac enzymes, such as CK, and by the disturbance in the patient's EKG, the QRS score. The graphics above suggest that the placebo group sustained more muscle damage. Stated differently, the CoQ/Taurine cocktail saved heart muscle from oxidative death. So, if heart muscle was saved, what effect was there on outcome?
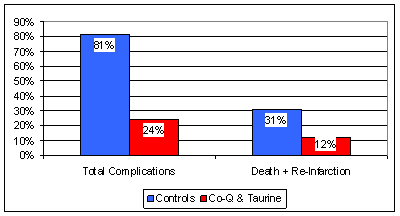
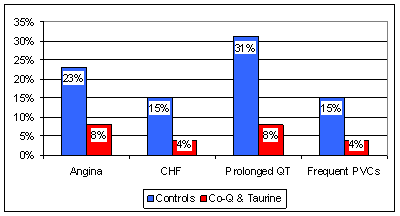
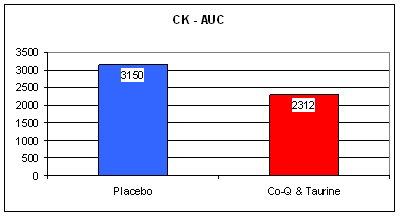
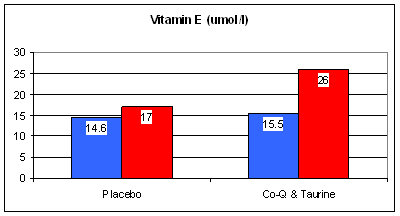 No
surprises here. Again, standard therapy plus the CoQ10/Taurine
supplementation was superior to standard drug therapy alone. Similar
studies have demonstrated similar benefits with antioxidant cocktails or fish
oil supplementation. These and other studies, published in the world
cardiology literature, suggest to me that integrating the best of nutritional
medicine with the best of drug medicine would save a lot of lives and a lot of
dollars. It is clear that CoQ10 supplementation is of value to the acute
heart attack patient in that:
No
surprises here. Again, standard therapy plus the CoQ10/Taurine
supplementation was superior to standard drug therapy alone. Similar
studies have demonstrated similar benefits with antioxidant cocktails or fish
oil supplementation. These and other studies, published in the world
cardiology literature, suggest to me that integrating the best of nutritional
medicine with the best of drug medicine would save a lot of lives and a lot of
dollars. It is clear that CoQ10 supplementation is of value to the acute
heart attack patient in that:
· Co-Q10 is a strong
antioxidant
· Co-Q10
stabilizes the cell membrane
· Co-Q10
is critical to energy generation
James C. Roberts MD FACC
1/01/07